Enhanced third-order optical nonlinearity driven by surface-plasmon field gradients
| Reviews and Highlights | Quantum Science | Molecular and Soft-matter | Ultrafast Nano-optics and Nanophotonics | Mineralogy and Geochemistry |
|---|
Vasily Kravtsov, Sultan AlMutairi, Ronald Ulbricht, A. Ryan Kutayiah, Alexey Belyanin, and Markus B. Raschke
Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 203903 (2018).
DOI PDF SI
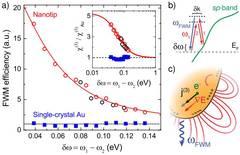
Achieving efficient nonlinear optical frequency conversion in small volumes is key for future on-chip photonic devices that would provide a higher-speed alternative to modern electronics. However, the already intrinsically low conversion efficiency severely limits miniaturization to nanoscale dimensions. Here we demonstrate that gradient-field effects can provide for an efficient, conventionally dipole-forbidden nonlinear response, offering a new approach for enhanced nonlinear optics in nanostructures. We show that a longitudinal nonlinear source current can dominate the third-order optical nonlinearity of the free electron response in gold in the technologically important near-IR frequency range where the nonlinearities due to other mechanisms are particularly small. Using adiabatic nanofocusing to spatially confine the excitation fields, from measurements of the 2ω1−ω2 four-wave mixing response as a function of detuning ω1−ω2, we find up to 10−5 conversion efficiency with a gradient field contribution to χ(3)Au of up to 10−19 m2/V2. The results are in good agreement with theory based on plasma hydrodynamics. Our results demonstrate an increase in nonlinear conversion efficiency with decreasing sample size that can offset and even overcompensate the volume decrease of conventional dipolar pathways. This will enable more efficient nonlinear optical devices and frequency converters and facilitate the extension of coherent multidimensional spectroscopies to the nanoscale.
