Quantification and coupling of the electromagnetic and chemical contributions in surface-enhanced Raman scattering
| Reviews and Highlights | Quantum Science | Molecular and Soft-matter | Ultrafast Nano-optics and Nanophotonics | Mineralogy and Geochemistry |
|---|
Yarong Su, Yuanzhen Shi, Ping Wang, Jinglei Du, Markus B. Raschke, and Lin Pang
J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 17505 (2019).
DOI PDF
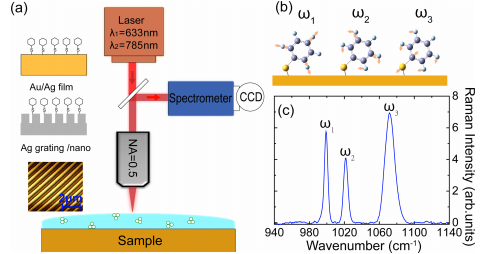
In surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), both chemical (CE) and electromagnetic (EM) field effects contribute to its overall enhancement. However, neither the quantification of their relative contributions nor the substrate dependence of the chemical effect have been well established. Moreover, there is to date no understanding of a possible coupling between both effects. Here we demonstrate how systematically engineered silver and gold planar and nanostructured substrates, covering a wide range of field enhancements, provide a way to determine relative contributions of chemical and electromagnetic field-enhancement in SERS measurements of benzenethiol. We find a chemical enhancement of 2 to 14 for different vibrational resonances when referencing against a vibrational mode that undergoes minimal CE. The values are independent of substrate type and independent of the enhancement of the electromagnetic intensity in the range from 1 to 106. This absence of correlation between chemical and electromagnetic enhancement resolves several long-standing controversies on substrate and intensity dependence of the chemical enhancement and allows for a more systematic design of SERS substrates with desired properties.
