Chemisorption energy of hydrogen on silicon surfaces
| Reviews and Highlights | Quantum Science | Molecular and Soft-matter | Ultrafast Nano-optics and Nanophotonics | Mineralogy and Geochemistry |
|---|
Markus B. Raschke and Ulrich Höfer
Phys. Rev. B 63, 201303 (2001).
DOI PDF
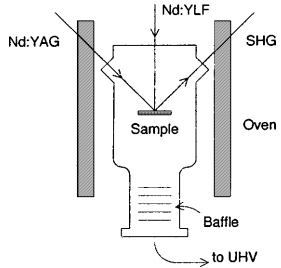
The chemisorption energy of H2on Si(111)7×7 and Si(001)2×1 was determined from thermodynamic equilibrium experiments in an ultrahigh vacuum quartz apparatus at temperatures of 760 to 970 K. The obtained values of 1.7±0.2 eV for Si(111) and 1.9±0.3 eV for Si(001) correspond to Si–H bond energies of 3.1 and 3.2 eV, respectively. Hydrogen bonding with silicon surfaces is thus found to be considerably weaker than in silane molecules and homologous clusters.
